Robust biosimilarity data?YES
See how Yesintek™ meets the FDA's rigorous approval standards for biosimilarity, plus their additional benchmark for interchangeability, based on the totality of evidence1,2
See how Yesintek™ meets the FDA's rigorous approval standards for biosimilarity, plus their additional benchmark for interchangeability, based on the totality of evidence1,2
YESINTEK is an interchangeable biosimilar to Stelara
Your patients can be switched from Stelara® (ustekinumab) to YESINTEK (ustekinumab-kfce), with no clinically meaningful differences in effectiveness and no increased safety risk.1
- YESINTEK was shown to be comparable to Stelara in treating patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis at Week 121
- Clinical efficacy was maintained for patients who continued on YESINTEK as well as for patients who switched from Stelara to YESINTEK after Week 161
Highly similar pharmacokinetics? YES1
Study design
STELLAR-1 was a Phase 1, randomized, double-blind, 3-arm, parallel-group study to compare the pharmacokinetic profile of YESINTEK with EU-approved and US-licensed Stelara in 258 healthy adult volunteers.1
YESINTEK concentration
- YESINTEK has a similar pharmacokinetic profile to EU-approved and US-licensed ustekinumab reference products1
- YESINTEK was generally safe and well tolerated by healthy volunteers in this Phase 1 PK study, with no reports of any unexpected AEs1
- Study drug for each arm was administered subcutaneously1
AE=adverse event; EU=European Union; PK=pharmacokinetic.
MEAN SERUM CONCENTRATION VS TIME PROFILE (PK ANALYSIS SET)
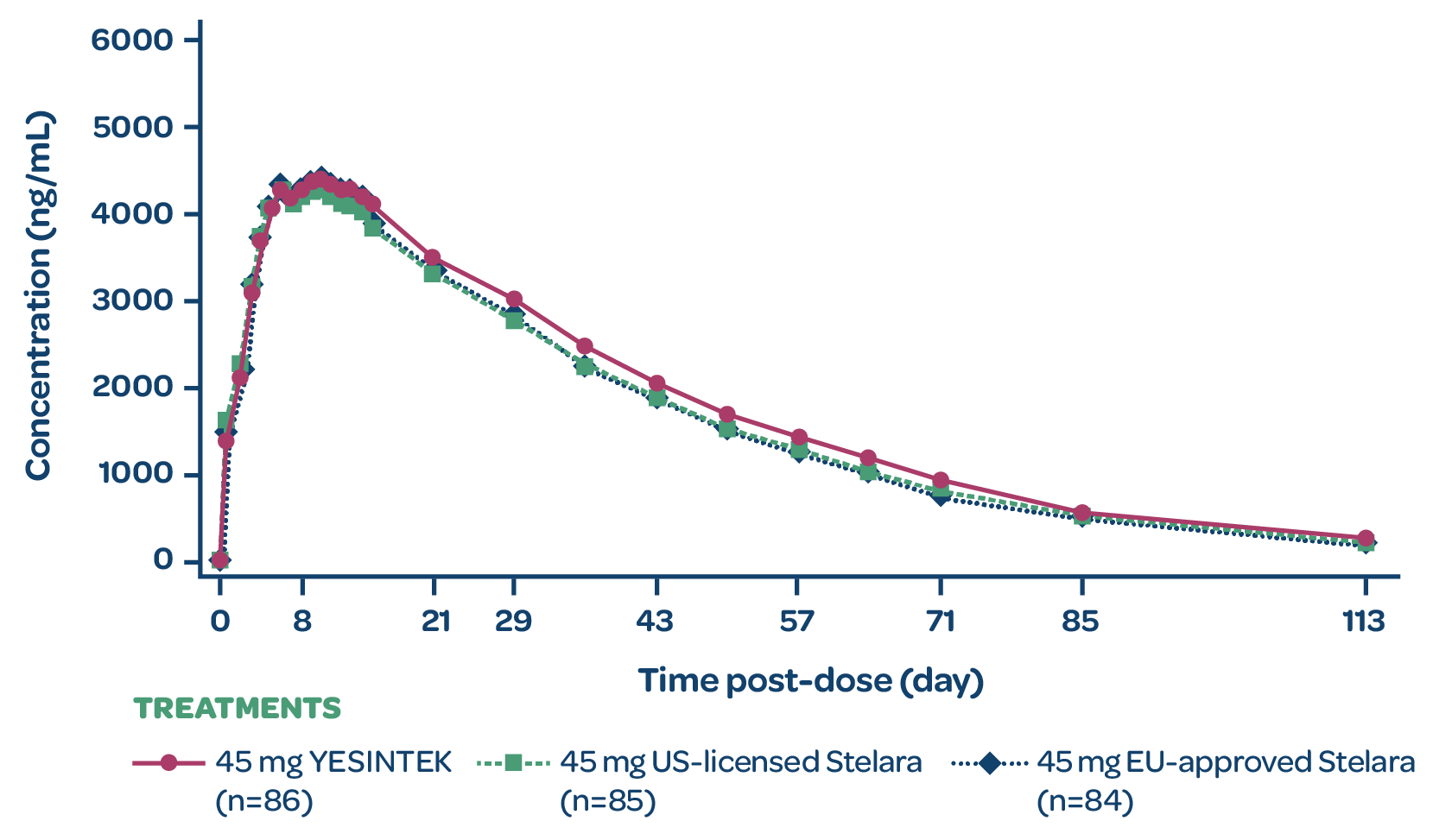
AE=adverse event; EU=European Union; PK=pharmacokinetic.
Highly similar efficacy? YES1
Study design
STELLAR-2 was a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter study to compare the efficacy and safety of YESINTEK and Stelara in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis.1
Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16. Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved PASI 75, entered treatment period 3 and continued the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.1
The primary efficacy endpoint was percentage change from baseline in the PASI score at Week 12. Secondary efficacy endpoints included percentage change from baseline in PASI score and raw PASI scores at Weeks 4, 8, 16, 20, 28, 40, and 52.1
STELLAR-2 was a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter study to compare the efficacy and safety of YESINTEK and Stelara in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis.1
Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16. Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved PASI 75, entered treatment period 3 and continued the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.1
The primary efficacy endpoint was percentage change from baseline in the PASI score at Week 12. Secondary efficacy endpoints included percentage change from baseline in PASI score and raw PASI scores at Weeks 4, 8, 16, 20, 28, 40, and 52.1
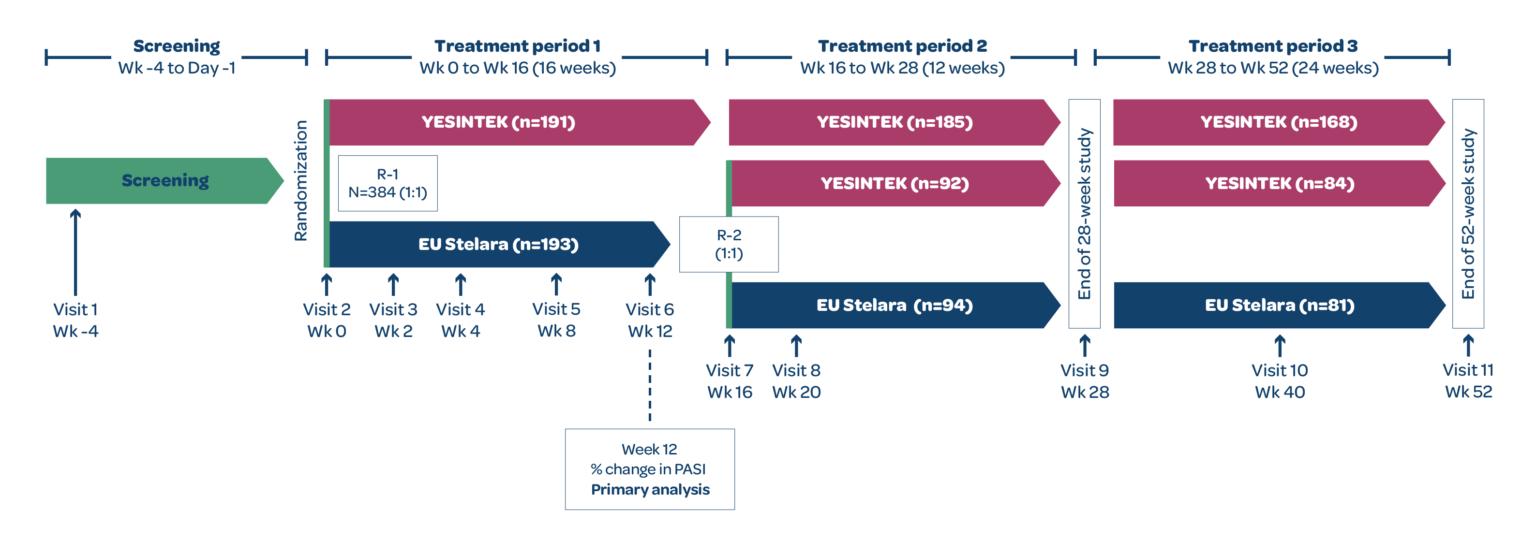
EU=European Union; PASI=Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; R=randomization.
PASI response rates
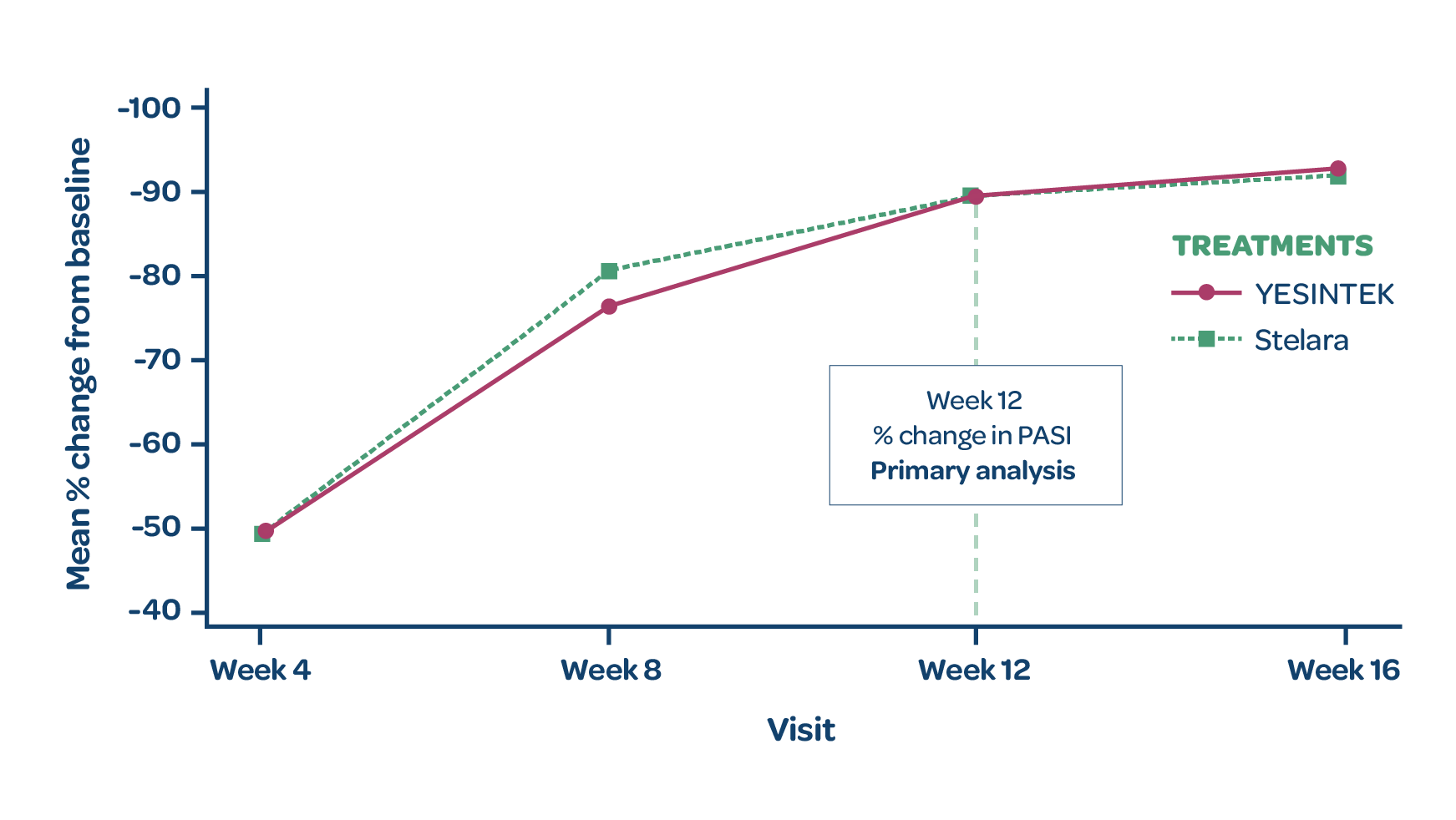
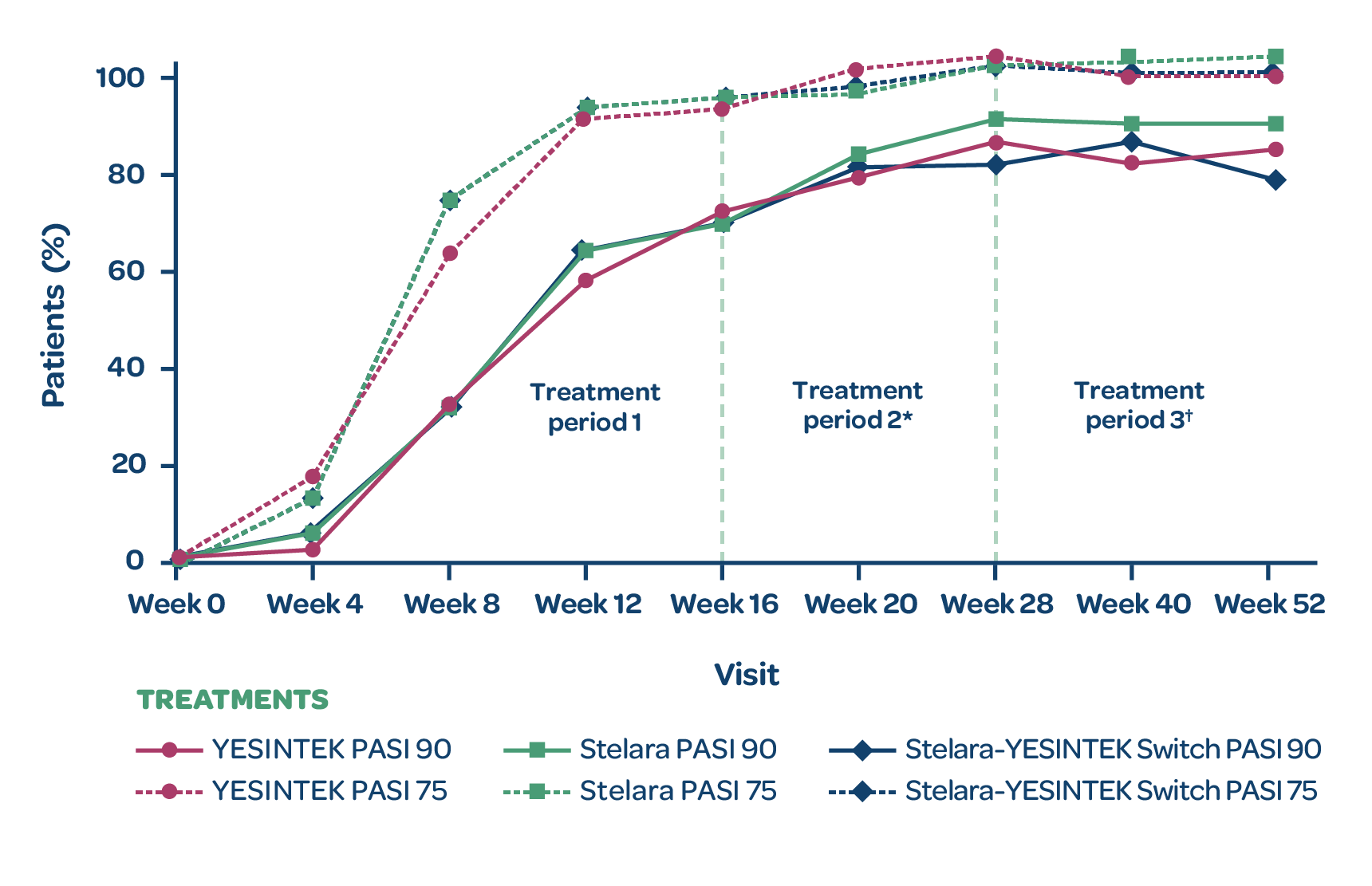
- There was no statistically significant difference in the % change from baseline in PASI scores between treatment groups at Week 12 (primary endpoint)1
- The proportion of patients with PASI 75 and PASI 90 responses through Week 52 were comparable among the treatment groups (secondary endpoints)1
- Switching from Stelara to YESINTEK had no significant impact on secondary efficacy scores1
*Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 by Week 12 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16.
†Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved at least PASI 75 response at Week 28 entered treatment period 3 to continue the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.
MEAN PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN PASI SCORE (FULL ANALYSIS SET)
PROPORTION OF PATIENTS WITH PASI 75 AND PASI 90
Study design
STELLAR-2 was a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter study to compare the efficacy and safety of YESINTEK and Stelara in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis.1
Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16. Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved PASI 75, entered treatment period 3 and continued the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.1
The primary efficacy endpoint was percentage change from baseline in the PASI score at Week 12. Secondary efficacy endpoints included percentage change from baseline in PASI score and raw PASI scores at Weeks 4, 8, 16, 20, 28, 40, and 52.1
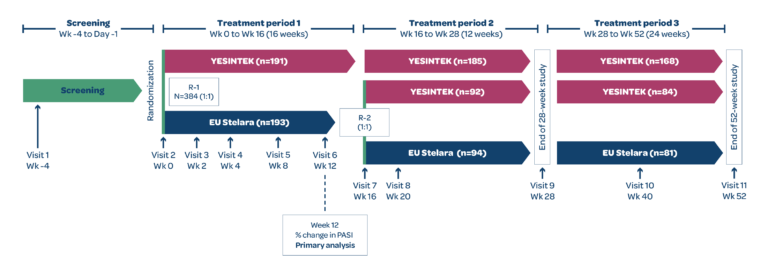
EU=European Union; PASI=Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; R=randomization.
PASI response rates
- There was no statistically significant difference in the % change from baseline in PASI scores between treatment groups at Week 12 (primary endpoint)1
- The proportion of patients with PASI 75 and PASI 90 responses through Week 52 were comparable among the treatment groups (secondary endpoints)1
- Switching from Stelara to YESINTEK had no significant impact on secondary efficacy scores1
*Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 by Week 12 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16.
†Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved at least PASI 75 response at Week 28 entered treatment period 3 to continue the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.
MEAN PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN PASI SCORE(FULL ANALYSIS SET)

PROPORTION OF PATIENTS WITH PASI 75 AND PASI 90

*Patients who completed treatment period 1 with Stelara and achieved PASI 50 by Week 12 were rerandomized 1:1 to receive YESINTEK or Stelara at Week 16.
†Patients who completed treatment period 2 and achieved at least PASI 75 response at Week 28 entered treatment period 3 to continue the same treatment until the end of the study (Week 52). For patients who were not eligible to enter treatment period 3, the end of study visit occurred in Week 28.
Highly similar safety profile? YES1
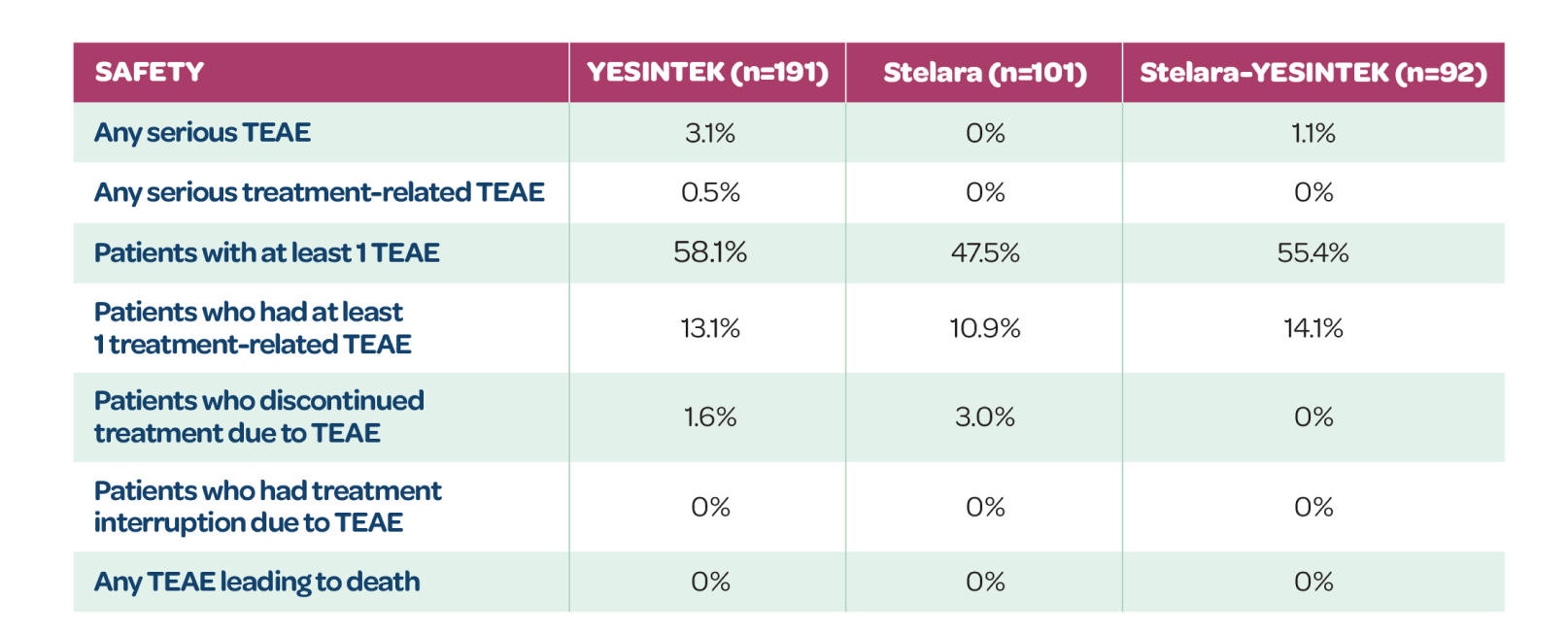
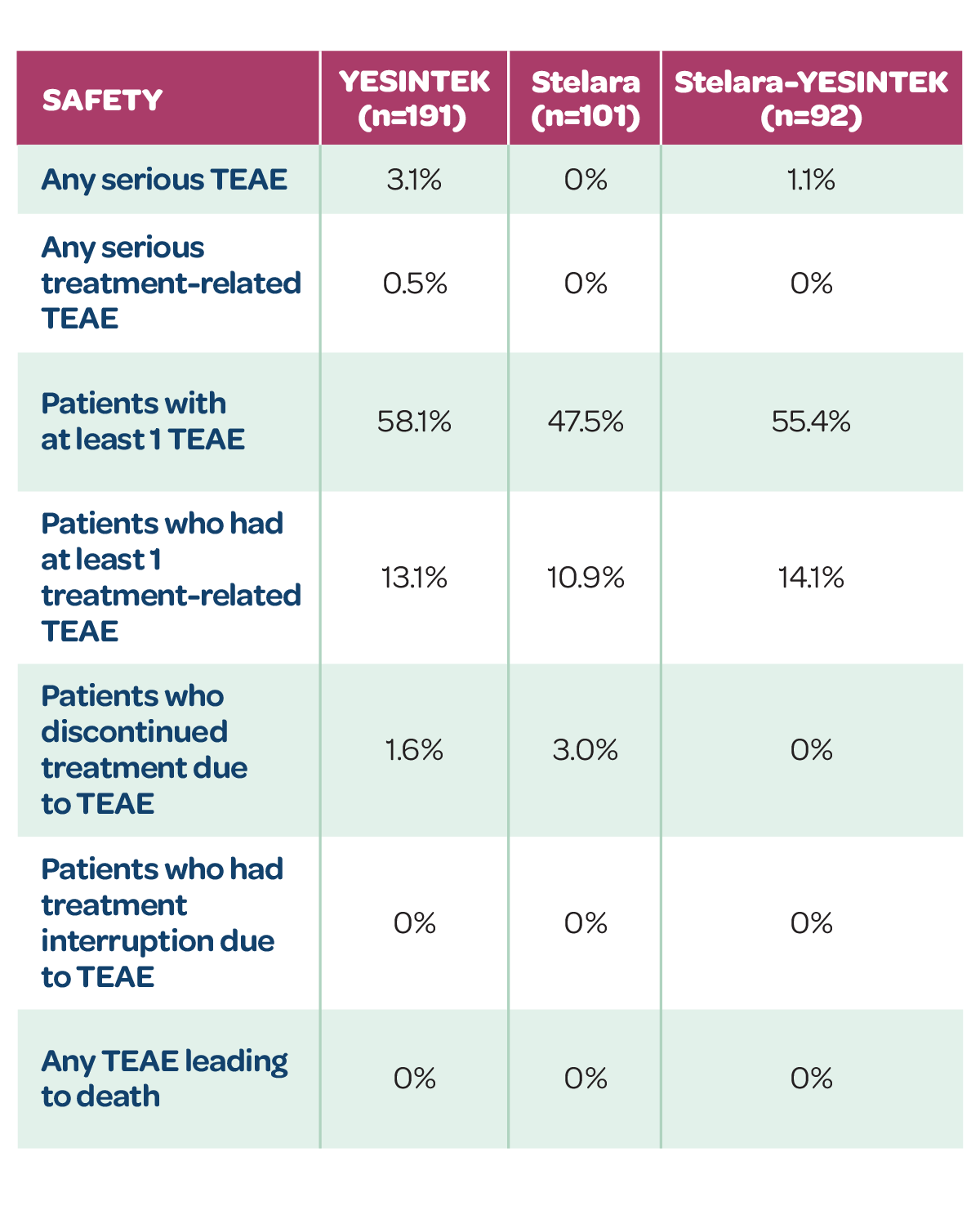
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs)
- YESINTEK has a well-tolerated safety profile, similar to Stelara1
- Switching from Stelara to YESINTEK caused no clinically meaningful differences in safety events1
TEAEs IN PATIENTS ON SAME TREATMENT THROUGH WEEK 52
TEAEs IN PATIENTS ON SAME TREATMENT THROUGH WEEK 52
Highly similar immunogenicity? YES1
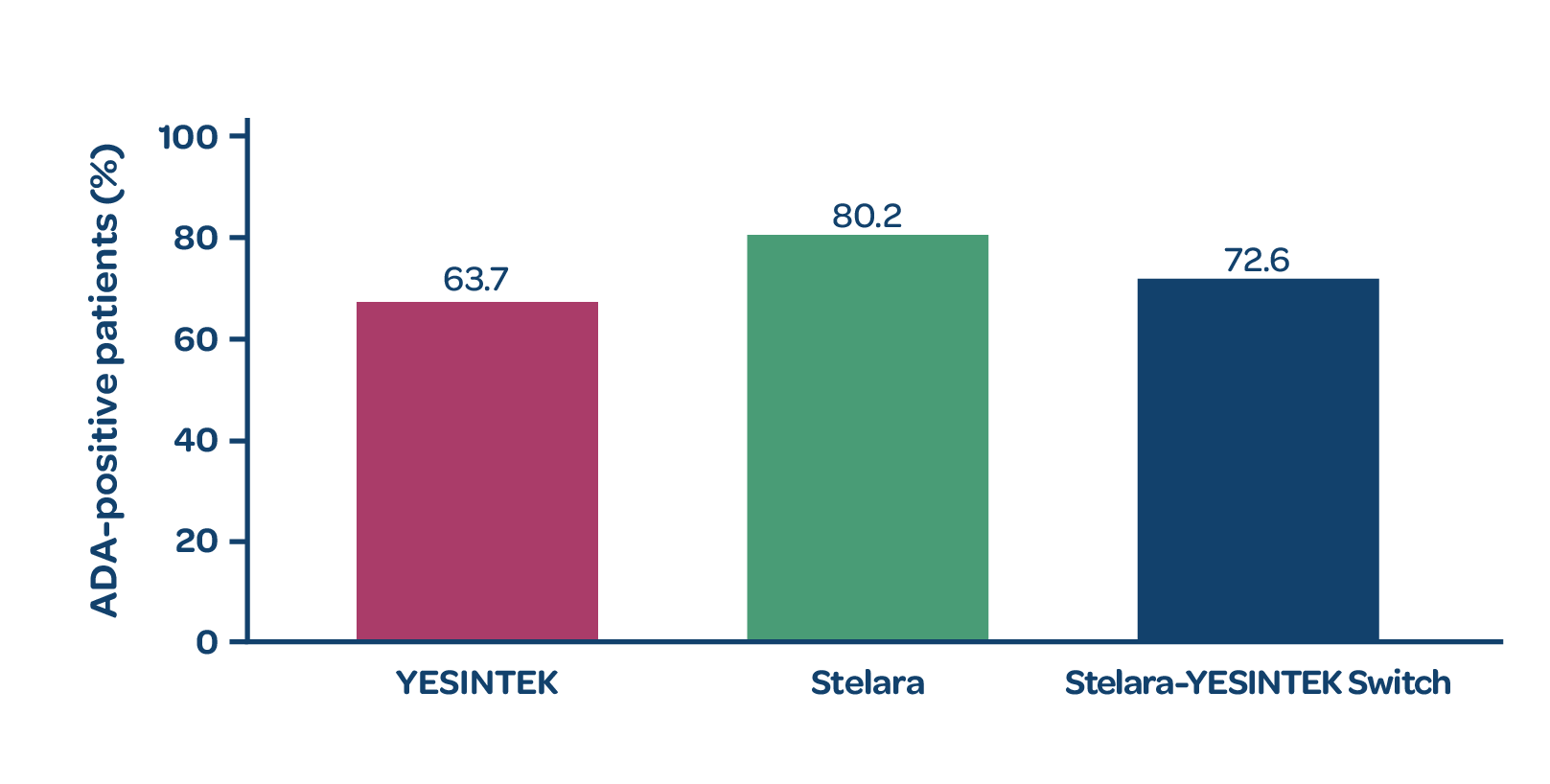
Antidrug antibodies (ADAs)
- The proportion of ADA-positive patients was comparable between the 2 treatment groups at Week 521
- Switching from Stelara to YESINTEK did not increase immunogenicity1
PROPORTION OF ADA-POSITIVE PATIENTS AT WEEK 52
REFERENCES
1. Data on file. Biocon Biologics; 2024. 2. US Food and Drug Administration. Biosimilars: review and approval. Last updated December 13, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/biosimilars/review-and-approval